In House Lab Work
Precise Diagnoses: Our In-House Lab Work for Pet Health!
Ensuring Your Pet’s Health: The Role of In-House Lab Work
At Edmonton Spay and Neuter Clinic, we prioritize your pet’s well-being. Our commitment extends beyond routine check-ups and surgical procedures. One essential aspect of our comprehensive veterinary services is in-house lab work. Let’s explore why this diagnostic tool is crucial for your furry companion’s health.


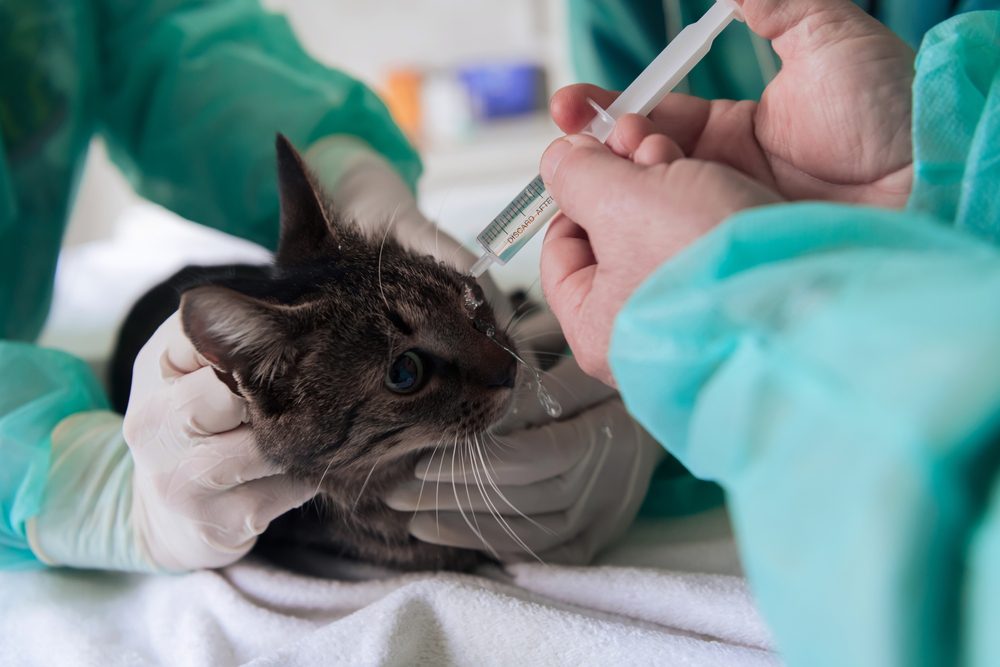

Schedule an Appointment Today
If your pet companion requires lab work or any other veterinary service, don’t hesitate to contact us. Our friendly and knowledgeable staff are always happy to answer your questions and schedule an appointment at your convenience.
Understanding Lab Work Procedures
Veterinary laboratory work involves diagnostic tests and procedures performed on samples from animals. These samples—such as blood, urine, feces, and tissue—help us diagnose, monitor, and treat various health conditions. In-house lab work allows us to obtain rapid results, enabling timely decision-making for your pet’s care.
The Importance of Lab Work
Early Detection and Prevention:
Lab work helps us identify health issues early. Detecting infections, organ dysfunction, or underlying diseases allows for prompt intervention.
Regular lab screenings are essential for preventive care. By monitoring trends in your pet’s health markers, we can address potential problems before they escalate.
Customized Treatment Plans:
Each pet is unique. Lab work allows us to tailor treatment plans based on individual needs.
Whether it’s adjusting medications, recommending dietary changes, or monitoring chronic conditions, lab results guide our decisions.
Common Laboratory Tests in Veterinary Medicine:
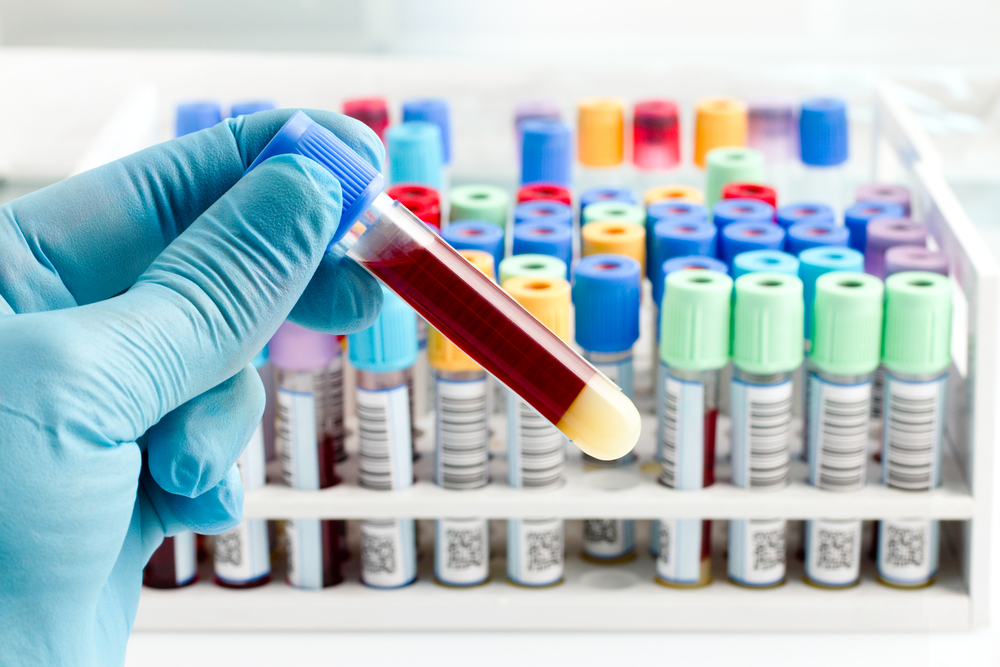
Blood Tests:
Evaluate overall health, organ function, and detect diseases.
Assess liver and kidney function, blood cell counts, and electrolyte balance.
Urine Tests:
Detect urinary tract infections, kidney disease, and other urinary issues.
Assess hydration levels and screen for diabetes.
Fecal Tests:
Identify parasitic infections (such as worms) and bacterial imbalances.
Essential for deworming protocols.
Cytology:
Microscopic examination of cells.
Diagnose skin conditions, tumors, and infections.
Microbiology:
Culturing and identifying bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Crucial for diagnosing infections.
Histopathology:
Examination of tissue samples under a microscope.
Diagnose tumors, infections, and abnormalities.

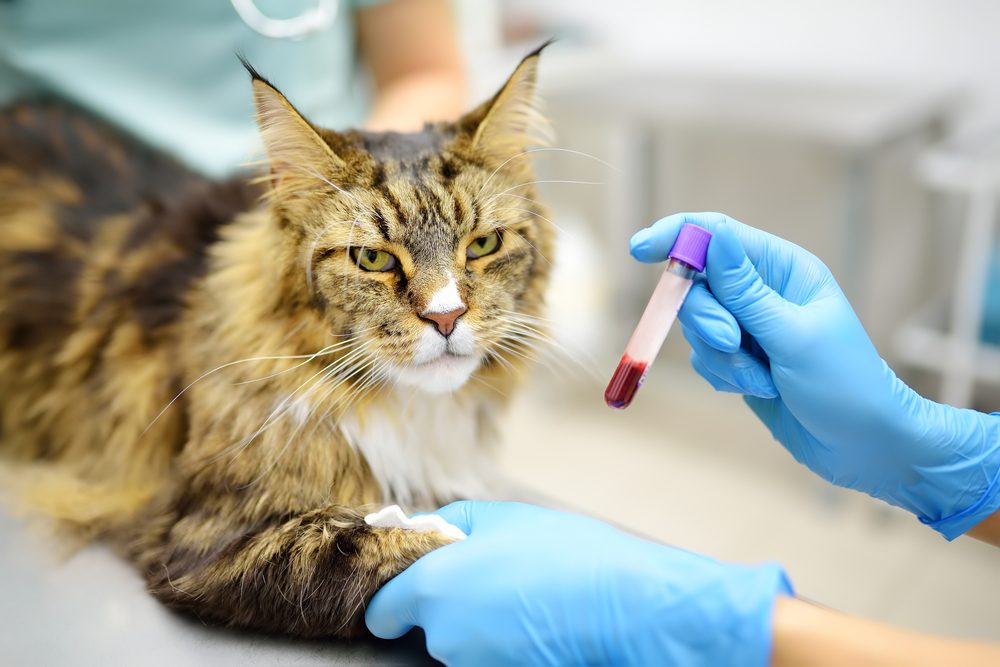

Why Choose Edmonton Spay and Neuter Clinic?
- Expertise: Our experienced veterinarians interpret lab results accurately.
- Holistic Approach: In-house lab work complements our other services, ensuring comprehensive care.
- Timely Decisions: Rapid results mean timely decisions for your pet’s health.
Schedule Your Pet’s Lab Work Today
Don’t wait until symptoms appear. Contact Edmonton Spay and Neuter Clinic to schedule in-house lab work. Let’s keep your pet healthy and thriving!
Feel free to reach out if you have any more questions or need emergency assistance !
